The female reproductive system is a complex and fascinating part of the human body. It is responsible for producing eggs, hormones, and menstrual cycles, as well as facilitating pregnancy and childbirth. In this blog post, we will explore some of the main features and functions of the female reproductive system, as well as some common health issues and tips for maintaining its well-being.
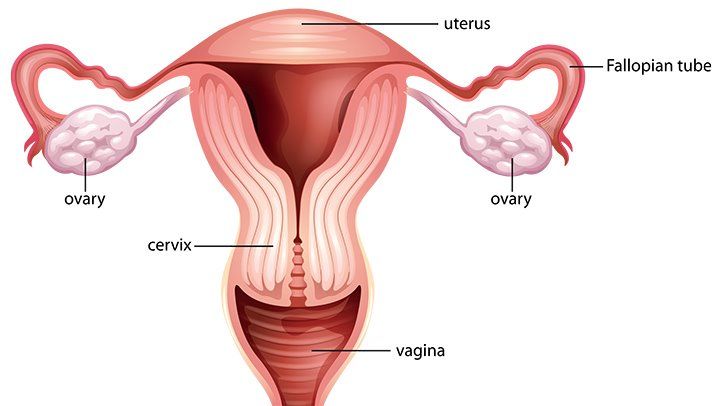
The female reproductive system consists of two main parts: the internal organs and the external genitals. The internal organs include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. The external genitals include the vulva, which consists of the labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and urethral opening.
The ovaries are two almond-shaped glands that produce eggs (also called ova) and hormones (such as estrogen and progesterone). The ovaries release one egg every month during a process called ovulation. The egg travels through the fallopian tube, which is a narrow tube that connects the ovary to the uterus. The uterus is a pear-shaped organ that houses and nourishes a developing fetus during pregnancy. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. The vagina is a muscular canal that connects the cervix to the outside of the body. It serves as a passage for menstrual blood, sperm, and babies.
The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia that surrounds the opening of the vagina. It consists of two pairs of skin folds: the labia majora (the larger outer folds) and the labia minora (the smaller inner folds). The labia protect the vagina and the urethral opening, which is where urine comes out. The clitoris is a small, sensitive organ that is located at the top of the vulva. It has thousands of nerve endings and is involved in sexual arousal and pleasure.
The female reproductive system undergoes several changes throughout a woman’s life cycle. One of these changes is the menstrual cycle, which is a monthly series of hormonal and physical events that prepare the body for pregnancy. The menstrual cycle has four phases: follicular phase, ovulation phase, luteal phase, and menstrual phase.
– The follicular phase begins on the first day of menstruation and lasts until ovulation. During this phase, the pituitary gland (a small gland in the brain) releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth of several follicles (sacs containing eggs) in the ovaries. One of these follicles becomes dominant and produces estrogen, which causes the lining of the uterus (called endometrium) to thicken.
– The ovulation phase occurs around day 14 of the cycle (depending on its length) and lasts for about 24 hours. During this phase, the dominant follicle releases an egg into the fallopian tube. This is when a woman is most fertile and can conceive if she has sexual intercourse with a male partner.
– The luteal phase begins after ovulation and lasts until menstruation. During this phase, the ruptured follicle transforms into a structure called corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone maintains the thickened endometrium and prepares it for implantation of a fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates and progesterone levels drop.
– The menstrual phase occurs when there is no fertilization or implantation. It usually lasts for about 3 to 7 days and involves shedding of the endometrium along with blood and mucus through the vagina. This is also known as menstruation or period.
The female reproductive system can be affected by various health issues, such as infections, hormonal imbalances, cancers, endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), fibroids, infertility, and more. Some of these issues can cause symptoms such as pain, bleeding, discharge, itching, swelling, irregular periods, acne, weight gain or loss, mood swings, etc. Some of these issues can also affect a woman’s ability to conceive or carry a pregnancy to term.
To maintain a healthy female reproductive system, it is important to practice good hygiene habits (such as washing regularly with mild soap and water), use protection during sexual intercourse (such as condoms or birth control pills), get regular check-ups and screenings (such as Pap smears or mammograms), eat a balanced diet (rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats), exercise regularly (at least 30 minutes a day), manage stress levels (through meditation, yoga, hobbies), avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.